PHENYLALANINE & TYROSINE
- Tyrosine (a non-essential amino acid) is produced from phenylalanine (an essential amino acid) by Phenylalanine Hydroxylase, a mixed function oxygenase (not a Hydroxylase, as the name implies).
Phenylalanine Hydroxylase
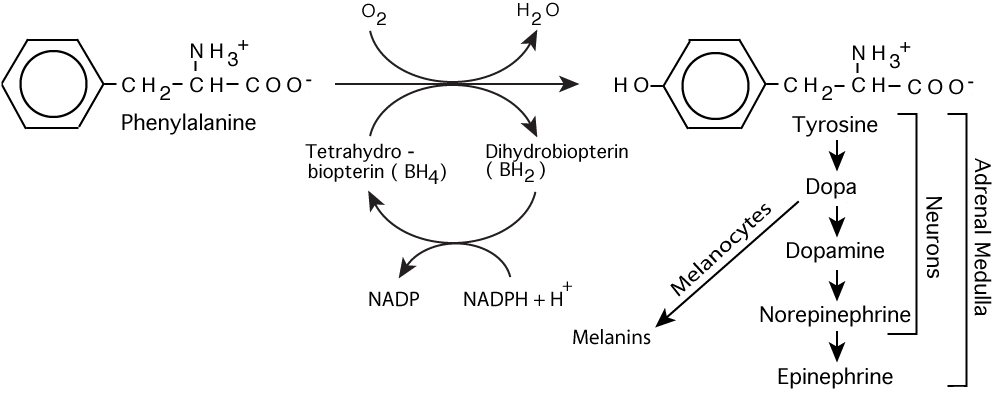
- O2 consumed, one oxygen atom donated to the hydroxyl group of tyrosine, the other donated to form water
- tetrahydrobiopterin, required as cofactor, donates two hydrogen atoms and is converted to dihydrobiopterin, requiring reconversion to tetrahydrobiopterin for the reaction to continue to produce tyrosine
- tyrosine degraded to fumarate (glucogenic) and acetoacetate (ketone body)
- normally, three quarters of phenylalanine in the body is converted to tyrosine
- Deficiencies of Phenylalanine Hydroxylase result in increased plasma levels of phenylalanine and several phenyl ketones and other products of phenylalanine metabolism, which are normally minor. The products, which become major, include phenylpyruvate (a phenyl ketone), resulting from transamination of phenylalanine, phenyllactate, resulting from the reduction of phenylpyruvate, phenylethylamine, resulting from the decarboxylation of phenylalanine and phenylacetate, resulting from the decarboxylation of phenylpyruvate or the oxidation of phenylethylamine and which causes a peculiar odor.
Phenylalanine Concentrations: Normal, Hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA), Phenylketonurea (PKU) Compound
ConcentrationNormal Benign HPA Variant HPA Classic HPA /
Classic PKUPhenylalanine approx. 1 mg/dL
(0.061 mM)4-10 mg/dL
(0.242 - 0.605 mM)10- 20 mg/dL
(0.605 - 1.21 mM)above 20 mg/dL
(above 1.21 mM)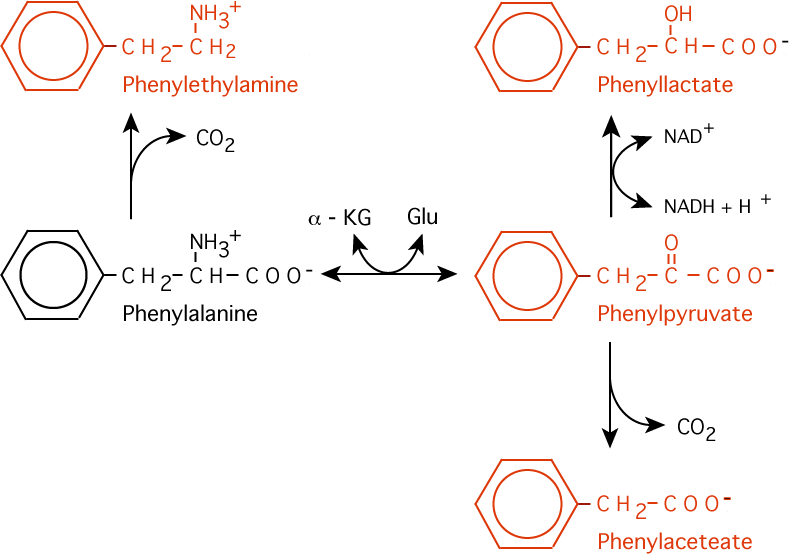 Minor metabolic products of phenylalanine metabolism become major products when phenylalanine hydroxylase is deficient. Phenylpyruvate is the phenylketone.
Minor metabolic products of phenylalanine metabolism become major products when phenylalanine hydroxylase is deficient. Phenylpyruvate is the phenylketone. - Phenylketoneurea (PKU), the major metabolic disease resulting from Phenylalanine Hydroxylase deficiency.
- autosomal recessive
- The frequency of PKU in the United States is currently considered to be one per 10,000 to one per 12,000 live births. The frequency varies in different ethnic groups. For example, it is one per 2,500 live births in Turkey and one per 4,000 live births in Ireland. In the United States, the frequency of PKU is one per 20,000 live births in California, compared with a frequency of one per 12,000 live births in Massachusetts.
- carriers have reduced phenylalanine hydroxylase
- Almost all untreated phenylketonurics are severely mentally retarded; about 1% of all patients in mental institutions have phenylketonuria.
- Brain weight of phenylketonurics is below normal; myelination of nerves is defective; life expectancy is drastically shortened — half are dead by age 20, three quarters are dead by age 30.
- Current hypothesis regarding PKU disease mechanism: Phenylalanine is a large, neutral amino acid (LNAA). LNAAs compete for transport across the blood–brain barrier (BBB) via the large neutral amino acid transporter (LNAAT). If phenylalanine is in excess in the blood, it will saturate the transporter. Excessive levels of phenylalanine tend to decrease the levels of other LNAAs in the brain.
- Defects in the reduction of dihydrobiopterin (rare) also cause phenylketonuria.
- Treatment is a low phenylalanine-content diet beginning soon after birth to minimize mental retardation along with supplementary tyrosine.
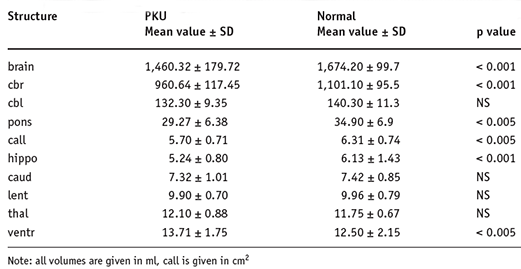 Comparison of brain weight between normal and PKU patients. Stefan Hahnela, Brain MRI Abnormalities in Phenylketonuria, Clinical Neuroradiology Volume 18, Number 1 / March, 2008
Comparison of brain weight between normal and PKU patients. Stefan Hahnela, Brain MRI Abnormalities in Phenylketonuria, Clinical Neuroradiology Volume 18, Number 1 / March, 2008
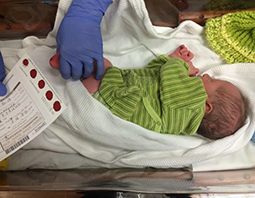 Guthrie Card: Blood is taken by heal stick from newborns and spotted onto an absorbent paper card that is sent to a diagnostic laboratory, where tests for various disorders are performed.
Guthrie Card: Blood is taken by heal stick from newborns and spotted onto an absorbent paper card that is sent to a diagnostic laboratory, where tests for various disorders are performed.Testing
The Guthrie test, also called the PKU test, is a diagnostic tool to test infants for phenylketonuria a few days after birth. Robert Guthrie invented the test in 1962 in Buffalo, New York. After his first success testing for PKU, Guthrie developed paper cards, called Guthrie Cards, which are thick, absorbent papers each with a metal blade to puncture an infant's heel and places for spotting infant blood. The New York State Newborn Screening Program effectively identifies babies with certain disorders and is required for all newborns born in New York unless the parents confirm, in writing, that they have a religious objection. The blood-spotted Guthrie Card is sent to the New York State Testing Laboratories in Albany, where the testing is performed; the blood is used to screen for approximately 50 different disorders, most of which are genetic disorders.